Modern microscopes are marvels of optics and technology which allow us to view minute details of cells with great clarity while others permit us to observe living organisms at incredible magnification.

Have you ever wondered the following simple questions: Do microscopes invert images? Which kind of microscopes inverts images? This article discusses answers to these questions and much more. Read on.
Some microscopes invert images because they have multiple lenses and an increased level of magnification, including compound microscopes. They form enlarged, inverted, and real images. However, quite a few microscopes do not invert images including dissecting microscopes. The term inverted microscope does not refer to image inversion.
Why Do Microscopes Invert Images?
An image is inverted because of the reflection of light rays and because it goes through two lens systems: the objective lens and the ocular lens.
Let’s discuss these in detail.
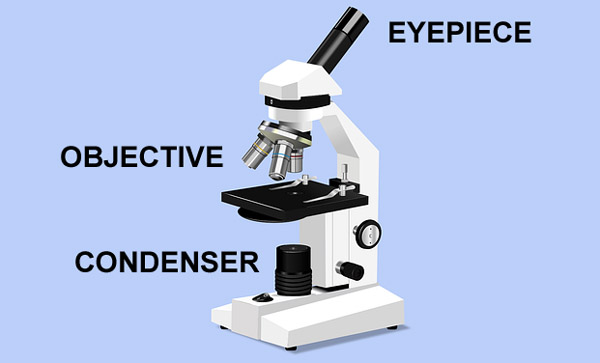
The most essential components of an optical microscope are objectives. These microscope objectives are responsible for the creation of a primary image. Plus, they play a very important part in determining the quality of images that the optical microscope can produce.
The objective is positioned near the specimen being observed and produces the first enlarged image of the object.
Also called an eyepiece, an ocular lens is where you look through to observe the sample. It enlarges the image formed by an objective lens so that you can see it.
The image will first pass through the objective lens and then the ocular lens, and the image will be inverted because of the objective lens’ curvature. The second lens further enlarges the inverted image that is projected from the first lens.
Both objective and ocular lenses are important to have to produce the proper magnification of the image. Most of the magnification happens within the objective lens.
Light Sources and Condensers
The light source, such as a light-emitting diode or an electric lamp, is there under the slide on which the specimen is being enlarged, and it illuminates the sample on the stage.
Condensers are lenses that gather and concentrate light from the illuminator into the sample. They are located below the stage and ensure that sharp images are created with a high magnification.
The light source under the stage helps you view the sample better. This light is then refracted. The light rays converge to produce an upside-down image once the light comes out of the other side.
The focal lengths of a lens determine the magnification of an image. The focal length is a measurement of how powerfully a system diverges or converges light. Magnifying power shares an inverse relationship with the focal length of the lens. The longer the focal length of the lens, the smaller the magnifying power of the microscope.
There are negative and positive focal lengths. Lenses are diverging lenses if they yield a negative focal length. And converging lenses always have positive focal lengths. A positive focal length forms a real image.
Do Dissecting Microscopes Invert Images?
Dissecting microscopes, also called stereo microscopes, do not invert the image of the sample under view because they have a lower total magnification. A dissecting microscope has two separate objectives and eyepieces and a low magnification range (between 10x and 40x).
It gives you an enlarged three-dimensional view of the sample so that you can see more fine details. The two eyepieces see the same object at a different angle, producing the 3D effect.
Compared to other microscopes, the stereo microscope utilizes the reflected light from the sample.
A dissecting microscope is called so because it is often used to conduct the dissection of a sample. This low-power microscope lets you see live samples and carry out dissections under the microscope.
It is often used for the purposes of examining large samples, such as plant parts, insects, and rocks.
Applications of a dissecting microscope
-
Stereo microscopes are used in forensic engineering.
-
Dissecting microscopes are used for examining fractures.
-
These low-power microscopes are used for inspecting circuit boards and watches.
-
Stereo microscopes are used for studying the surfaces of solid objects.
-
Dissecting microscopes are used for microsurgical procedures and dissection.
Advantages of a dissecting microscope
-
Stereo microscopes are used to observe complete samples and not in pieces.
-
Dissecting microscopes are easy to use and carry.
-
It is an important microscopic technique because it can be used in a variety of fields.
Disadvantages of a dissecting microscope
-
Dissecting microscopes are expensive to buy.
-
These microscopes cannot be used to observe tissue structures because they have a low magnification power.
Is an Inverted Microscope One That Inverts Images?
In an inverted microscope, the condenser and the light source are above the stage pointing downwards, while the objectives are hidden under the stage pointing up.
This is a reverse construction of normal conventional microscopes, where the objective lenses are on top of the specimen stage while the source of light and the condenser are under the specimen stage. So, with this microscope, you see the image from down upwards instead of seeing the image from up downwards.
The inverted microscope uses light rays to focus on a sample to create an image that you can see through the objective lenses. The condenser lens focuses the light on the sample or object.
The objectives, which are situated below the specimen stage, collect light from the condenser, enlarging the image, which is then sent to the eyepiece lens. The eyepiece lens reflects the light through a mirror. You can easily see the cells through the bottom of the cell culture vessel.
Uses of an inverted microscope
An inverted microscope is mainly used for diagnosis, identification, and sample preparation. Because of its versatility, it can be used for a wide range of tasks. Disintegrated or dried parts of organisms that cannot be seen using the conventional microscope methods can be seen using an inverted microscope.
-
Inverted microscopes are used to view living organisms or cells found at the bottom of Petri plates or cell culture flasks.
-
They are useful in assessing nematology specimens.
-
Inverted microscopes are used in fungal cultural diagnoses.
Advantages of an inverted microscope
-
An inverted microscope lets you view more specimens in a shorter period of time.
-
The risk of crashing an objective into the specimen is less with an inverted microscope.
-
These microscopes save you money and time in the preparation of a specimen.
-
You have larger working distances and can image big specimens as the specimen is above the objective.
-
You can use an inverted microscope to observe cells in large amounts of the medium.
Disadvantages of an inverted microscope
-
The biggest downside is the cost. An inverted microscope is costly to construct and is more complex.
Check out this video to learn about inverted microscopes.
Do Compound Microscopes Invert Images?
Compound microscopes invert images because of their increased level of magnification and two lenses. The image viewed with compound microscopes is two-dimensional.
Also known as a biological microscope, a compound microscope uses a compound lens system to offer magnification in the ranges of 40x-1000x. It consists of two lenses, an objective lens (near the object) and an eye lens (near the eye). While these two lenses produce high magnification, a condenser below the sample stage concentrates the light directly into the specimen.
A compound microscope is also called a high-power microscope because of its high magnification, and it’s often used to observe living cells.
Uses of a compound microscope
-
Compound microscopes are used for medical and forensic research. They help in the identification of diseases in pathology laboratories. Forensic laboratories use these high-power microscopes to identify human fingerprints.
-
Compound microscopes are used in schools for educational purposes.
-
These biological microscopes are used to detect the presence of metals.
-
They are used to observe viruses and bacteria.
Advantages of a compound microscope
-
Compound microscopes are easy to handle.
-
They have their own light source in their base.
-
You can get detailed information about the specimen due to the usage of two or more lenses.
Disadvantages of a compound microscope
-
The specimen can be magnified to a certain extent. It cannot be observed once this limit is achieved.
Learn more about compound microscopes in this video.
Final Thoughts
Microscopes lets you view things you could never see before. We use them to study molecular structures, microorganisms, and cells and their components. In fact, these optical instruments are not just used to observe microbes and bacteria but are also used in several industries.
A lot of industries use these tools for several purposes like manufacturing processes, quality control, and inspection. Additionally, microscopes are used to diagnose diseases and other conditions in hospitals.
There are many different types of microscopes, such as inverted microscopes, dissecting or stereo microscopes, and compound microscopes, to name a few. And some microscopes produce an inverted image like compound microscopes.
Click on the following link to learn how to make microscope slide mounting medium.
